Read more about this post…
Credits: Source
Disclaimer
Read more about this post…
Credits: Source
Disclaimer
Identification of atazanavir as a pan-positive allosteric modulator for family A GPCRs that stabilizes a unique GPCR-G protein-β-arrestin megacomplex and mediates sustained signaling.
Read more about this post…
Credits: Source
Disclaimer
 Ancient tools from central China are flipping the script, revealing early humans were far more innovative than history once gave them credit for. Archaeologists working at a newly excavated site in central China are changing long-standing ideas about how early hominins lived and adapted in East Asia. The discoveries suggest these ancient populations were […]
Ancient tools from central China are flipping the script, revealing early humans were far more innovative than history once gave them credit for. Archaeologists working at a newly excavated site in central China are changing long-standing ideas about how early hominins lived and adapted in East Asia. The discoveries suggest these ancient populations were […]
Read more about this post…
Credits: Source
Disclaimer
This study aimed to evaluate the biological effects of three calcium silicate-based materials-Biodentine XP (BD-XP), TheraCal PT (THPT), and TheraBase Ca (THB)-on human dental pulp stem cells (hDPSCs), focusing on cytocompatibility, immunomodulatory behavior (via IL-6 expression), and odontogenic/mineralization potential compared to control conditions. hDPSCs were cultured with eluates (25%, 50%, 100%) of BD-XP, THPT, and THB. Cytocompatibility was assessed via metabolic activity assay, cell cycle analysis, and cell migration. Morphology and adhesion were examined by SEM, while surface composition was analyzed by EDX. IL-6 secretion was quantified using ELISA. Gene expression of odontogenic/osteogenic markers (ALP, DSPP, RUNX2, COL-1) was analyzed via qRT-PCR at 14 and 21 days. Alizarin Red S staining was used to assess mineralization. Results were compared to unconditioned and osteogenic controls (p < 0.05). All materials exhibited acceptable cytocompatibility. BD-XP promoted the highest cell viability, migration, and adhesion. IL-6 secretion was significantly reduced in all treated groups, most notably with THB. SEM and EDX showed strong cell attachment and calcium-rich surfaces for BD-XP. BD-XP significantly upregulated DSPP and RUNX2 at both time points and COL-1 at day 21. ALP expression was mainly observed in the positive control. BD-XP also showed the greatest mineralized nodule formation. Biodentine XP demonstrated the most favorable biological behavior, showing high cytocompatibility, upregulation of odontogenic markers, and enhanced mineralization. These results highlight its potential for clinical use in vital pulp therapy and regenerative endodontics.
Keywords:
calcium silicate‐based materials; dental pulp reparation; vital pulp materials.
Read more about this post…
Credits: Source
Disclaimer
 A new brain study suggests that different kinds of memory may rely on the same underlying brain systems, a finding that could reshape how scientists understand and study memory. Instead of using separate brain regions to retrieve different types of information, the brain appears to draw on overlapping areas regardless of the kind of memory […]
A new brain study suggests that different kinds of memory may rely on the same underlying brain systems, a finding that could reshape how scientists understand and study memory. Instead of using separate brain regions to retrieve different types of information, the brain appears to draw on overlapping areas regardless of the kind of memory […]
Read more about this post…
Credits: Source
Disclaimer
This study aimed to evaluate the biological effects of three calcium silicate-based materials-Biodentine XP (BD-XP), TheraCal PT (THPT), and TheraBase Ca (THB)-on human dental pulp stem cells (hDPSCs), focusing on cytocompatibility, immunomodulatory behavior (via IL-6 expression), and odontogenic/mineralization potential compared to control conditions. hDPSCs were cultured with eluates (25%, 50%, 100%) of BD-XP, THPT, and THB. Cytocompatibility was assessed via metabolic activity assay, cell cycle analysis, and cell migration. Morphology and adhesion were examined by SEM, while surface composition was analyzed by EDX. IL-6 secretion was quantified using ELISA. Gene expression of odontogenic/osteogenic markers (ALP, DSPP, RUNX2, COL-1) was analyzed via qRT-PCR at 14 and 21 days. Alizarin Red S staining was used to assess mineralization. Results were compared to unconditioned and osteogenic controls (p < 0.05). All materials exhibited acceptable cytocompatibility. BD-XP promoted the highest cell viability, migration, and adhesion. IL-6 secretion was significantly reduced in all treated groups, most notably with THB. SEM and EDX showed strong cell attachment and calcium-rich surfaces for BD-XP. BD-XP significantly upregulated DSPP and RUNX2 at both time points and COL-1 at day 21. ALP expression was mainly observed in the positive control. BD-XP also showed the greatest mineralized nodule formation. Biodentine XP demonstrated the most favorable biological behavior, showing high cytocompatibility, upregulation of odontogenic markers, and enhanced mineralization. These results highlight its potential for clinical use in vital pulp therapy and regenerative endodontics.
Keywords:
calcium silicate‐based materials; dental pulp reparation; vital pulp materials.
Read more about this post…
Credits: Source
Disclaimer
Background:
Skin and soft tissue infections (SSTIs) impose a substantial global and regional burden, and their management is increasingly complicated by antimicrobial non-susceptibility. In Saudi Arabia, data remain fragmented, with few studies providing species-level analyses stratified by specimen type and infection depth.
Methods:
We retrospectively analyzed 6,760 wound and tissue specimens (2016-2024) from a tertiary hospital in Riyadh, Saudi Arabia. Organisms were identified using standard microbiological methods and VITEK 2. Antimicrobial susceptibility testing was interpreted according to CLSI M100, defining non-susceptibility as resistant or intermediate categories. Binary logistic regression was used to assess temporal trends in antimicrobial non-susceptibility, with year of isolation entered as a continuous predictor.
Results:
Gram-negative organisms predominated (63.2%), followed by Gram-positives (35.6%) and yeast (1.2%). Staphylococcus aureus was the leading pathogen (28.8%), with methicillin resistance detected in 39.0% of isolates. Escherichia coli (14.7%) and Pseudomonas aeruginosa (12.1%) were also common. Among Enterobacterales, 26.9% were extended-spectrum β-lactamase (ESBL) producers and 16.1% were carbapenem-resistant Enterobacterales (CRE). P. aeruginosa showed high carbapenem non-susceptibility. Tissue-derived isolates demonstrated significantly higher meropenem non-susceptibility than swab Isolates (20.3% vs. 16.4%, p = 0.027), although Enterobacterales subsets occasionally showed the reverse pattern. Temporal analysis revealed rising non-susceptibility to amikacin, ceftriaxone, imipenem, and meropenem (p < 0.05), while oxacillin resistance in S. aureus and clindamycin non-susceptibility in Gram-positives declined over time.
Conclusion:
Gram-negative organisms predominated in SSTIs, showing rising non-susceptibility to amikacin and carbapenems. Separately, among Gram-positive pathogens, S. aureus exhibited a clear decline in oxacillin resistance. These shifts underscore the need for ongoing resistance surveillance.
Keywords:
Escherichia coli; Pseudomonas aeruginosa; Saudi Arabia; antimicrobial resistance; carbapenem-resistant Enterobacterales; methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus; multidrug resistance; non-susceptibility.
Read more about this post…
Credits: Source
Disclaimer
Postdoctoral fellow in neuroscience at Tulane University
A postdoctoral fellow position is available in the Department of Neurosurgery at Tulane University School of Medicine. The candidate will join the laboratory of Dr. Xiangming Zha in the Clinical Neuroscience Research Center in the Department of Neurosurgery.
The research areas include molecular signaling and neuroprotective mechanisms in neuron and/or endothelial cells, the contribution of brain acid signaling to ischemic stroke, blood brain barrier regulation, vascular cognitive impairment and dementia (VCID), and traumatic brain injury (TBI). The research will use in vitro techniques and in vivo mouse surgery models. A solid wet bench experience is required.
Qualifications:
1). Recent PhD or equivalent degree in neuroscience, molecular biology, physiology, or cerebral vascular biology. 2). Previous experience with rodent surgeries, including the mouse middle cerebral artery occlusion model or TBI models, relevant VCID models, transcriptome analysis and gene regulation is highly desirable. 3). Solid publication record.
The fellow will work closely with the Pl and others on the research team. We support the career progression of the fellow. We will provide guidance on career development and encourage the fellow to apply for postdoctoral fellowship as well as other career stage appropriate fundings..
Application Instructions
Interested candidates should submit an application package containing 1) CV, 2) contact information for three research references, and 3) a brief summary discussing your research interest or fit with the lab research. The package can be emailed, preferably as a single PDF file, to xzha@tulane.edu.
Read more about this position…
Credits: Source
Disclaimer
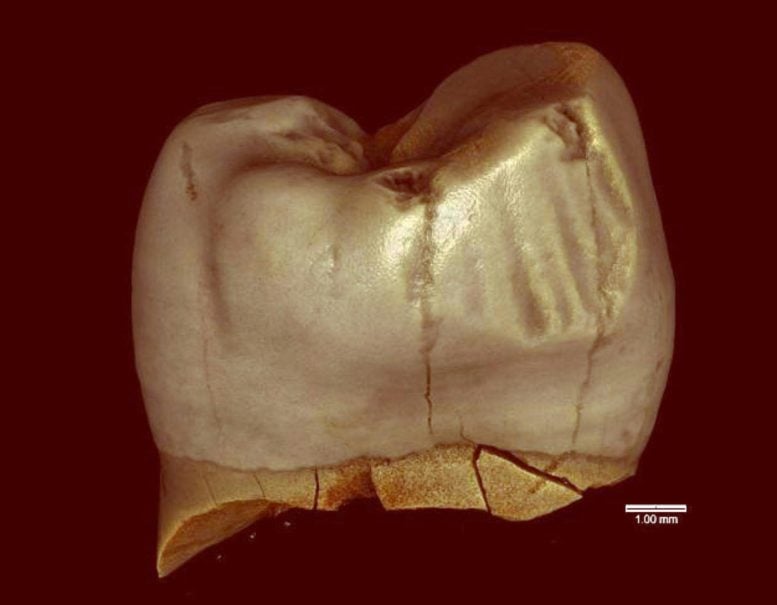 A large comparative study of primate teeth shows that grooves once linked to ancient human tooth-picking can form naturally, while some common modern dental problems appear uniquely human. For many years, narrow grooves found on ancient human teeth were widely interpreted as signs of intentional behavior, such as cleaning teeth with sticks or fibers, or […]
A large comparative study of primate teeth shows that grooves once linked to ancient human tooth-picking can form naturally, while some common modern dental problems appear uniquely human. For many years, narrow grooves found on ancient human teeth were widely interpreted as signs of intentional behavior, such as cleaning teeth with sticks or fibers, or […]
Read more about this post…
Credits: Source
Disclaimer